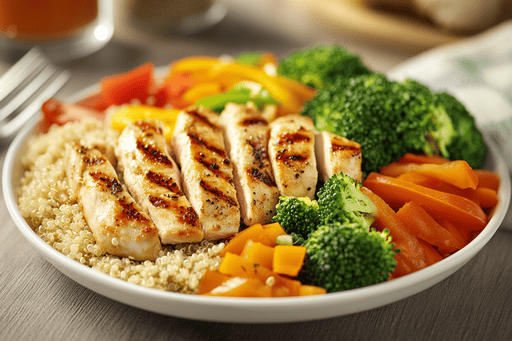Metabolism is the process that determines how quickly your body turns food into energy. When your metabolism works efficiently, your body burns calories faster, which helps maintain a healthy weight and energy levels. However, the speed of your metabolism depends on several factors, such as age, gender, and physical activity. But did you know that certain foods can help speed up your metabolism? In this article, we’ll look at which foods can boost your metabolism and help you maintain an active lifestyle.
How Metabolism Works
Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that take place in your body to sustain life. Every time you eat or drink, your body processes nutrients and converts them into energy. The speed at which this happens is what we call metabolism.
Several factors influence metabolic rate:
- Age: Metabolism slows down with age, making it harder to maintain weight as you grow older.
- Gender: Men typically have faster metabolisms due to having more muscle mass.
- Physical Activity: The more active you are, the faster your metabolism works.
Despite these natural factors, you can influence your metabolism through proper nutrition. Certain foods help increase thermogenesis—the process through which the body produces heat and burns calories.
Foods That Help Speed Up Metabolism
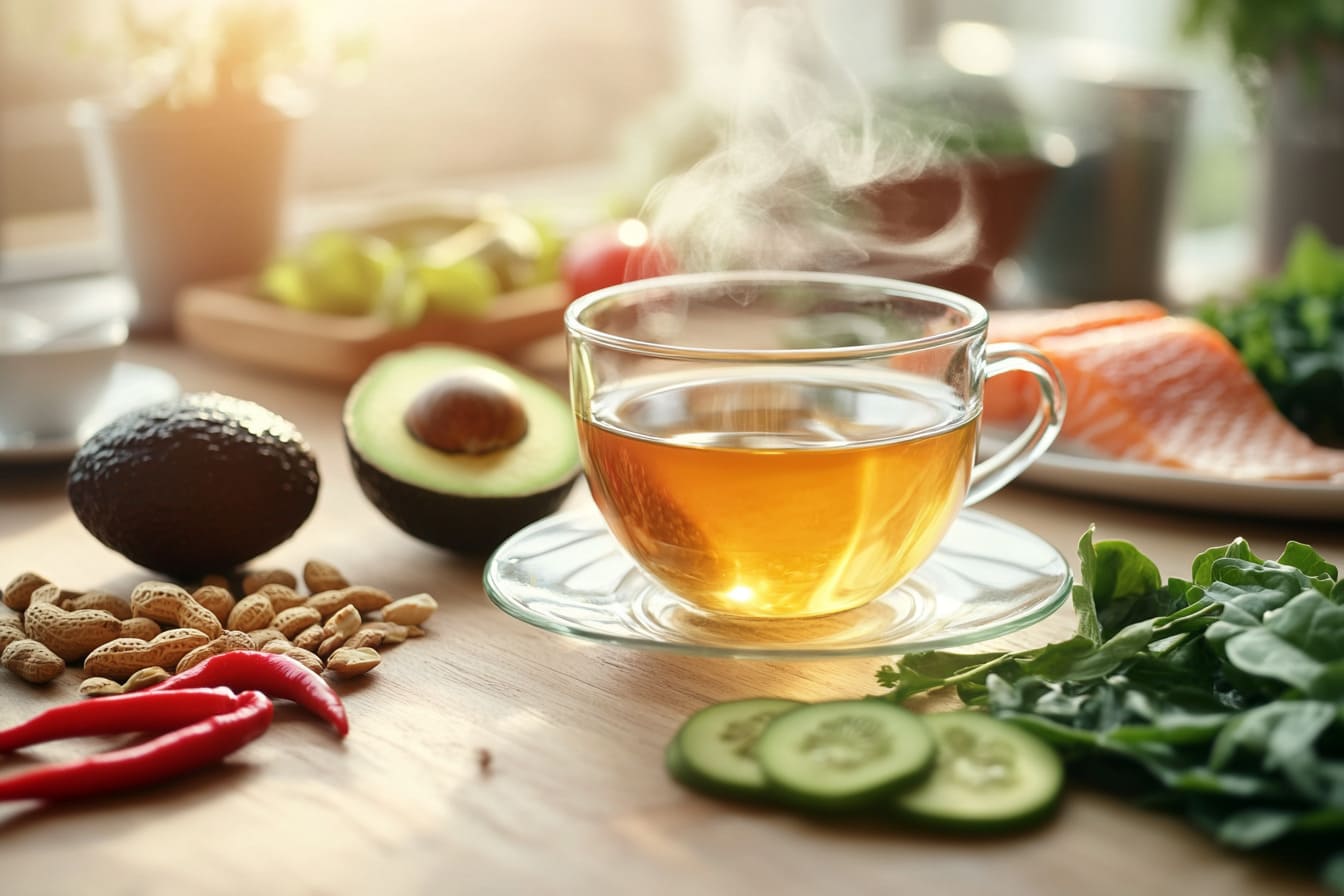
Spicy Foods
Spicy foods like chili peppers and cayenne contain capsaicin, a compound known to boost metabolism by increasing thermogenesis. Capsaicin triggers your body to produce more heat, which leads to burning more calories. Studies have shown that eating spicy foods can raise your metabolic rate by 8% for several hours after consumption. Adding peppers to your meals is an easy way to kickstart fat-burning without drastic changes to your diet.
Protein-Rich Foods
Foods high in protein, such as meat, fish, eggs, and legumes, stimulate thermogenesis more than carbs or fats. Digesting and absorbing protein requires more energy, which leads to a higher calorie burn—this is known as the thermic effect of food (TEF). The more protein you consume, the more calories your body burns to process it. Additionally, protein helps maintain and build muscle mass, which naturally boosts metabolism since muscle burns more calories than fat, even at rest.
Green Tea and Coffee
Green tea and coffee are two beverages well-known for their metabolic benefits. Green tea contains catechins—powerful antioxidants that can help increase fat burning. Research suggests that drinking green tea can boost metabolism by 4-5%.
Caffeine, found in both green tea and coffee, stimulates the central nervous system, increasing activity and energy expenditure. A few cups of coffee per day can significantly improve your metabolic rate and physical performance.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa are rich in complex carbohydrates and fiber, which take longer to digest and help regulate blood sugar levels. Your body burns more calories digesting fiber than it does processing refined carbs. Whole grains also keep you feeling fuller for longer, helping control appetite and promoting steady energy levels throughout the day.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, flaxseed, and walnuts, can help boost fat metabolism. Omega-3s not only benefit heart health but also help regulate insulin levels, improving your body’s ability to use energy efficiently. As a result, your metabolism speeds up, and your body burns more calories.
The Importance of Water for Metabolism
Drinking enough water is one of the simplest ways to boost metabolism. Dehydration can slow your metabolism because your body needs water to carry out all chemical processes, including burning calories. Studies show that drinking 500 ml of cold water can temporarily increase metabolism by 30% for about 30-40 minutes. This happens because your body expends energy to heat the water to body temperature.
How to Include Metabolism-Boosting Foods in Your Diet
Now that you know which foods help boost metabolism, here are some practical ways to incorporate them into your daily diet:
- Add spicy foods to your meals: Try adding cayenne pepper to soups, salads, or meat dishes. It's an easy way to enhance fat burning without making major changes to your diet.
- Eat more protein-rich foods: Aim to include protein in every meal. Eggs for breakfast, chicken for lunch, and fish for dinner will keep your metabolism active throughout the day.
- Switch to green tea or coffee: Replace sugary drinks or juices with green tea or coffee. Not only will it boost your metabolism, but it will also improve your overall well-being.
- Choose whole grains: Opt for oats, quinoa, or brown rice instead of white bread or refined carbs.
- Increase your intake of omega-3s: Incorporate salmon, tuna, or nuts into your meals. These foods will not only boost your metabolism but also support heart health.
Conclusion
Including metabolism-boosting foods in your diet can play a key role in maintaining a healthy weight and high energy levels. Adding spicy foods, protein, green tea, and omega-3s to your meals will help activate your metabolism and burn more calories. However, remember that for the best results, proper nutrition should be combined with physical activity and plenty of water.
FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
How quickly can foods boost metabolism?
The metabolism-boosting effects of foods can occur within hours of eating. For example, spicy foods and protein can increase thermogenesis for several hours after consumption.
Can foods alone lead to weight loss?
Metabolism-boosting foods can help burn more calories, but weight loss also depends on maintaining a calorie deficit and leading an active lifestyle.
How much coffee should I drink to boost metabolism?
Moderate consumption—2 to 3 cups per day—can help boost metabolism. However, excessive caffeine intake can lead to nervousness and disrupt sleep.
Can drinking water alone speed up metabolism?
Water can temporarily boost metabolism, but long-term results depend on maintaining a healthy diet and being physically active.
How often should I eat protein-rich foods to support metabolism?
It’s recommended to include protein in every meal to sustain thermogenesis and metabolic activity throughout the day.